DDQ TUE 2021-08-31
6. Physical Variations & Bias¶
6.1. Agenda¶
General Announcements
Activity
Category |
Assignment |
Day |
Date |
|---|---|---|---|
Term Project |
Milestone 1: Problem Proposal: Proposal |
FRI |
2021-09-03 |
Term Project |
Milestone 1: Problem Proposal: Revision1 |
MON |
2021-09-06 |
- 1
Remember, Dr. Cotterell has office hours at 9AM on MONs in Boyd 307 should your group have any last minute questions.
Category |
Assignment |
Day |
Date |
|---|---|---|---|
Paper Presentations |
FRI |
2021-09-03 |
6.2. Activity¶
6.2.1. Introduction¶
Duration: TBD
In the Handbook of Anthropometry, you can find research and data related to human dimensions, i.e., the measurements and proportions of the human body. For example, in John T. Manning’s chapter, “Sex Differences and Age Changes in Digit Ratios,” the author presents research related to digit ratios, specifically: how they differ by sex; and how some ratios might be linked to different diseases and disorders.
- digit ratio
Often taken to mean the ratio of the lengths of the second and fourth digits (2D:4D).
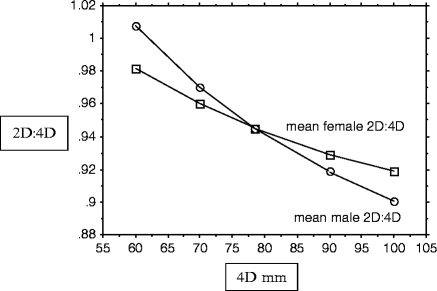
Fig. 6.1 Fig. 48.2: The relationship between 4D length and mean 2D:4D. The sample consisted of 344 males and 404 females. Note that 2D:4D showed no sex difference at the value of 4D where male and female regression lines for 2D on 4D intersect (in this case at 78.47 mm). Below this value of 4D, females had lower 2D:4D than males. Above this value, they had higher 2D:4D than males and the sex difference in 2D:4D increased in size with increasing 4D.¶
If digit ratios can differ between different groups of users, then they might be worth considering when it comes to planning multi-touch user interfaces (e.g., many touch screens) or even single-touch user interfaces (e.g., keyboards). The placement of icons, buttons, and other “things” that users must press their fingers against could potentially lead to bias, i.e., the interface design favors some groups of users over others.
What questions should be considered to mitigate biases based on physical variations among our users? That’s the topic of today’s DDQ.
6.2.2. Breakout Groups¶
Important
RANDOMIZE: Please move around to different tables and form a random group for this activity.
Quickly introduce yourselves to each other, if you don’t already know each other.
Pick a group representative. This person will be responsible for posting your breakout group’s response on Piazza before breakout group work ends for this activity.
Help your group representative respond to the following in a followup discussion to Piazza @22.
List the names of your breakout group members.
Without realizing it, biases can manifest themselves in our designs. List two or three ways the members of your breakout room might personally but unintentionally introduce bias based on physical diversity into a design.
Search the Web for an example where a human-computer interface failed to respond to some of the physical variations in its users. Provide a link and briefly summarize the scenario, including descriptions of any issues your example caused.
What are some things we should consider to avoid what happened in your example provided in (b)? In other words, how might we preemptively respond to physical diversity in our designs?
Who benefits from these consideration? For each stakeholder you identify, please provide a brief justification.
Look at and reply to the posts that other groups made.
6.2.4. After Class¶
Before 11:55PM today, individually comment on another group’s post by replying to their followup discussion in Piazza @22.
Continue reading the Foundations module, and make sure you’re aware of current assignments and their due dates.
Comments
Please keep the comments polite and constructive. In addition to whatever else you want to write, please comment on one aspect of a group’s post that you like and one aspect that you think needs improvement (e.g., you find that something is unclear or you don’t understand a justification). As always, be sure to provide a brief justification for each.